Rules
What is the rules
The HTTP Rules engine allows users to customize the CDN edge server behavior, e.g. how the CDN will manage cache and redirection. This creates a lot of flexibility and adaptability for different platform websites to integrate with CDN without much hassle.
How to set the rules
You can go to CDN Resources -> Rules to configure.
A condition consists of a subject, which determines the value to select, and a predicate, which specifies what to compare the subject against. Conditions are bonded by the connectives “AND” or “OR”. When all the conditions are met, the CDN edge server will perform the actions associated with the rule. The CDN edge server processes these rules from top to bottom order. It ends processing on the first match.
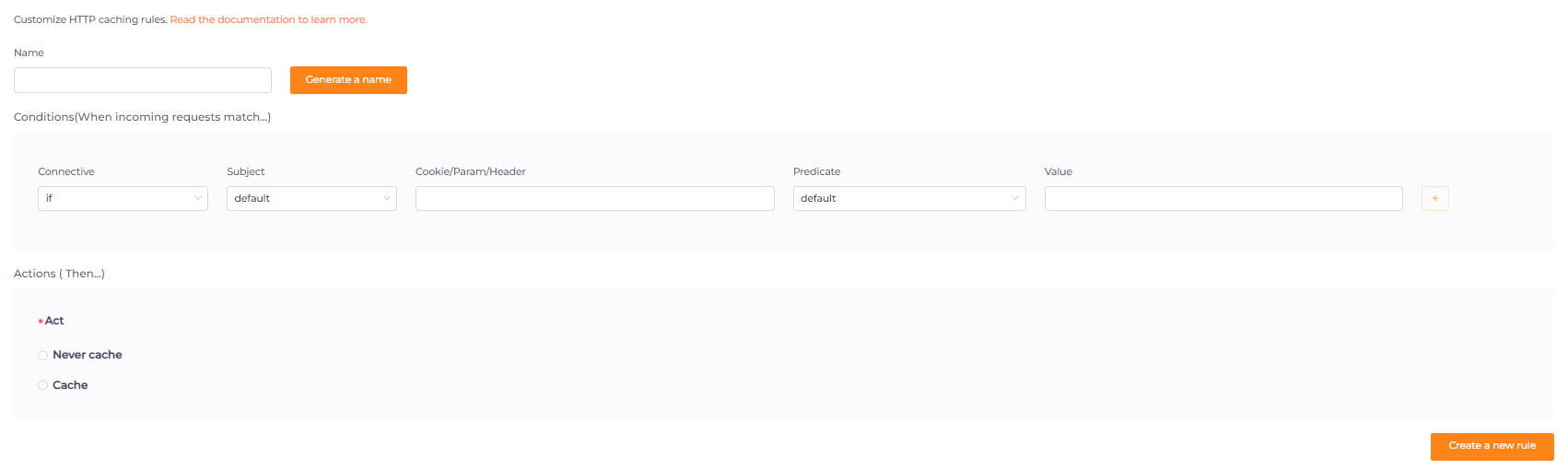
Subject
| Subject | Details |
|---|---|
| URL | Select the requested URL section. The complete request URL, including protocol, domain name, request path, parameters, etc. Example http://cdn.example.com/image.jpg?name=cdn |
| IP | Selects the IP address of the client. If the clients use a proxy server, the IP of their proxy server which made the request to the edge server will be selected. Example 192.0.2.43 |
| Cookie | Selects the value of a specific cookie sent by the client. Example Cookie chosen: logged_inClient request header: Cookie: session_id=abcdef;logged_in=1; cart_id=defabcSelected value: 1 |
| Country | Selects the client’s country. If the client’s country cannot be derived from their IP, the value “ ” is selected. Example Client’s IP: 193.113.9.162Selected value: United Kingdom |
| Param | Selects the value of a specific query string parameter. If there are multiple identical keys, the last value is selected. Example Parameter chosen: pageClient requests: http://cdn.example.com/index.php?page=about&id=53Selected value: about |
| Extension | Selects the file extension of the request. If the request filename does not contain a dot, then the value “ ” is selected. Example Client requests: http://cdn.example.com/image.jpgSelected value: jpg |
| Header | Selects the value of a specific client request header. If the request header does not exist, then the value “ ” is selected. Example Header chosen: User-AgentClient sends header: User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3) Firefox/30.0Selected value: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3) Firefox/30.0 |
| Scheme | Selects the scheme part of the request. It can be either http or https. Example Client requests: http://cdn.example.com/image.jpgSelected value: httpExample Client requests: https://secure.example.com/image.jpgSelected value: https |
Predicates
| Predicate | Details |
|---|---|
| Equals | Compares the subject to an exact value. Example URL /index.phpEquals /index.phpResult TRUEURL /ExampleFile.txtEquals /examplefile.txtResult TRUEURL /image.jpgEquals /index.phpResult FALSE |
| Starts with | Compares whether the subject starts with a value. Example IP 192.0.2.54Starts With 192.0.2.Result TRUEURL /images/files.jpgStarts With /images/Result TRUEIP 192.5.54.3Starts With 192.0.2.Result FALSE |
| Ends with | Compares whether the subject ends with a value. Example URL /images/files.jpgEnds With .jpgResult TRUEURL /videos/video.mp4Ends With .jpgResult FALSE |
| In List | Compares the subject to the list of values. Each value is separated by a single space. Example Country GBIn List GB ES FR DEResult TRUECountry USIn List GB ES FR DEResult FALSE |
| Matches wildcard | Compares whether the subject matches a wildcard value. The wildcard character * matches any 0 or more characters. Multiple *s can be specified.Example Url /images/photos/photo.jpgMatches Wildcard /images/ * .jpgResult TRUEUrl /images/videos/video.mp4Matches Wildcard /images/ * .jpgResult FALSEUrl /archives/2014/news/index.htmlMatches Wildcard / * /2014/news/ *Result TRUE |
| Does not equal | Opposite of the Equals value |
| Is not in list | Opposite of the In list value |
| Does not match wildcard | Opposite of the Matches wildcard value |
Actions
| Action | Details | |
|---|---|---|
| Cache rules | ||
| Force Edge To Never Cache | Forces the CDN edge server to never cache the request. However, if the request is already cached (for example, if it was cached prior to setting up this rule), it will not be forced out of cache. | |
| Force Edge To Cache | Forces the CDN edge server to cache the request for a specified duration. This overrides any Cache-Control or Expires headers from the origin, even if they specify private or no-cache.The value must be 1 second or longer. |
|
| Force Client To Cache | Forces the client to cache the request for a specified duration. This is achieved by removing all Cache-Control and Expires response headers, sending instead “Cache-Control: max-age=...”.The value must be 1 second or longer. | |
| Redict rules | ||
| Forbid Client | Returns a simple 403 Forbidden response to the client. | |
| Redirect Client from HTTP to HTTPs | Returns a 301 Redirect response from http address to https address instead of loading from cache or upstream.Note that in the case of multiple CDN hostname, it is necessary to select the hostname that performs redirection. | |
| Redirect Client | Returns a 302 Redirect response to the client, to the specified URL.The URL must be specified in full, starting with http:// or https:// |
|
| Modify header | ||
| Set Request Header | Overrides a request header to the origin. A header name and header value must be provided. | |
| Set Response Header | Overrides a response header to the client. A header name and header value must be provided. | |
| Set Client IP In Request Header | Sets the client’s IP address in a request header to the origin. A header name must be provided. | |
| Origin rules | ||
| Prepend Origin Directory | Prepends a directory to the URL when the edge server requests it from the origin. Examples Prepend origin directory imagesClient requests to edge: http://cdn.example.com/photo.jpgEdge requests to origin: http://cdn.example.com/images/photo.jpgPrepend origin directory: /some/sub%20directory/Client requests to edge: http://cdn.example.com/some/file.txtEdge requests to origin: http://cdn.example.com/some/sub%20directory/some/file.txt
|
|
| Origin Server Hostname | The choice of origin server hostname affects the domain name received when requesting the origin. The default is CDN acceleration domain name. Follow CDN Hostname: "Follow CDN Hostname" refers to keeping the domain name received by the source site consistent with the current CDN hostname. This type is mainly used when the source site supports multi domain hosting, accurately matching requests and avoiding 404/400 errors. Follow Origin: "Follow Origin" refers to the domain name received by the source site still being the information filled in the source site address, and not changing with the proxy service domain name. It is mostly used for source sites that only serve a single domain name, with good compatibility and no need to modify the origin configuration. Customization: Custom Host content supports request variables. |
|
| Automatically add headers | Automatically add these headers to the origin to facilitate the origin in obtaining client information. |